Madhava KrishnaE-commerce & Q-commerce, Lean Six SigmaLeave a comment0
Tired of customer complaints about late deliveries and inaccurate orders? Lean Six Sigma provides the tools to transform your logistics and order fulfillment into a customer-centric powerhouse.
Introduction
Logistics and order fulfilment are the lifeblood of e-commerce businesses. However, inefficiencies such as long lead times, high error rates, and inventory mismanagement can significantly impact profitability and customer satisfaction.
Lean Six Sigma—a methodology that combines Lean’s focus on waste reduction with Six Sigma’s emphasis on defect minimization—offers a structured approach to solving these challenges. By applying Lean Six Sigma principles, e-commerce companies can optimize their logistics processes, reduce costs, and enhance customer experiences.
This blog explores specific ways Lean Six Sigma can improve logistics and order fulfilment in e-commerce, supported by examples and a detailed case study using the DMAIC framework.
Key Applications of Lean Six Sigma in E-Commerce Logistics
Lean Six Sigma principles can be applied to various aspects of logistics and order fulfilment. Mentioned below are key ideas with real-world examples.
1. Reducing Order Fulfilment Errors
Example: A leading online retailer reduced picking errors by implementing barcode scanning technology and standardizing workflows. This resulted in a 20% improvement in order accuracy.
2. Optimizing Inventory Management
Example: A grocery delivery startup used demand forecasting tools to align inventory levels with customer purchasing patterns. This reduced overstocking by 15% and minimized waste.
3. Streamlining Last-Mile Delivery
Example: A Q-commerce (quick commerce) company optimized delivery routes using AI-powered algorithms, reducing delivery time by 25% during peak hours.
4. Improving Warehouse Layouts
Example: A fashion e-commerce company reorganized its warehouse layout using Lean principles, reducing worker travel time between picking zones by 30%.
Case Study: Applying DMAIC to Reduce Order Fulfilment Cycle Time

A mid-sized e-commerce company faced challenges with long order fulfilment cycle times, leading to delayed deliveries and customer dissatisfaction. Using the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) methodology, they achieved significant improvements.
Define Phase
- Problem Statement: The average order fulfillment cycle time was 48 hours, exceeding the industry benchmark of 24 hours.
- Goal: Reduce the cycle time to under 24 hours while maintaining order accuracy above 98%.
- Tools Used: SIPOC Diagram (Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, Customers) to map the entire fulfillment process.
Measure Phase
- Collected data on current cycle times for each process step (picking, packing, shipping).
- Measured key metrics like order accuracy rate (95%) and average picking time per item (12 minutes).
- Tools Used: Time-motion studies and Pareto charts to identify major contributors to delays.
Analyze Phase
- Identified bottlenecks in the picking process due to inefficient warehouse layouts and manual data entry errors during packing.
- Discovered that 60% of delays were caused by workers traveling long distances between picking zones.
- Tools Used: Root Cause Analysis (5 Whys), Value Stream Mapping.
Improve Phase
- Implemented a zone-based picking system to minimize worker travel distances.
- Introduced handheld barcode scanners for real-time inventory updates during packing.
- Automated repetitive tasks like printing shipping labels using robotic systems.
- Tools Used: Kaizen workshops for process redesign; simulation software to test new workflows.
Control Phase
- Established KPIs like average picking time per item (<8 minutes) and cycle time (<24 hours).
- Conducted weekly audits to ensure adherence to new processes.
- Deployed IoT sensors for real-time tracking of inventory movement within the warehouse.
- Tools Used: Control charts for monitoring performance trends; IoT dashboards for inventory tracking.
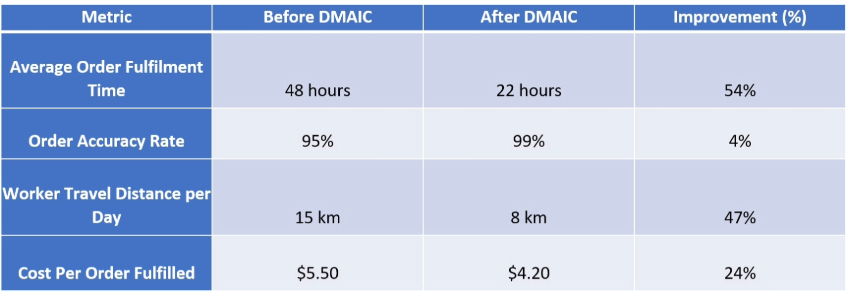
Key Quantifiable Benefits Achieved
By applying Lean Six Sigma principles through the DMAIC framework, the company achieved the following results:
Conclusion
Lean Six Sigma offers a powerful framework for addressing inefficiencies in logistics and order fulfillment within e-commerce businesses. Companies can achieve faster delivery times, lower costs, and higher customer satisfaction rates by focusing on waste reduction and defect minimization through tools like DMAIC.
Whether it’s optimizing warehouse layouts or leveraging automation technologies like IoT devices and AI algorithms, adopting Lean Six Sigma principles is essential for staying competitive in the fast-paced world of e-commerce. For businesses looking to scale efficiently while maintaining profitability in 2025, investing in Lean Six Sigma methodologies is not just an option—it’s a strategic imperative.
If you are interested to achieve similar success stories, write to us!


